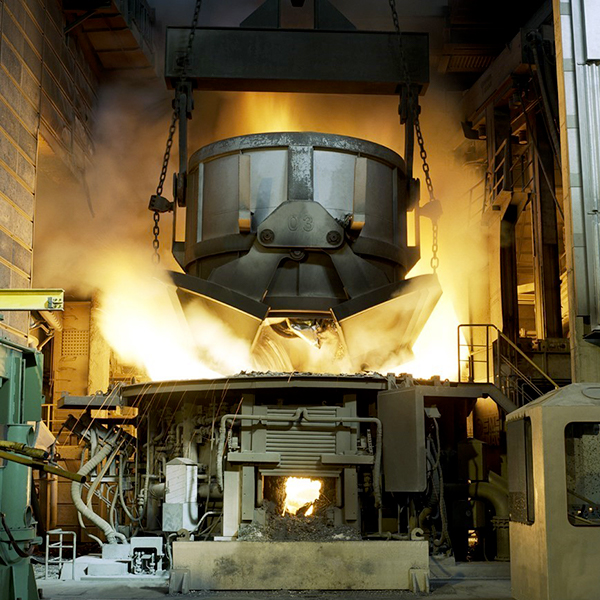
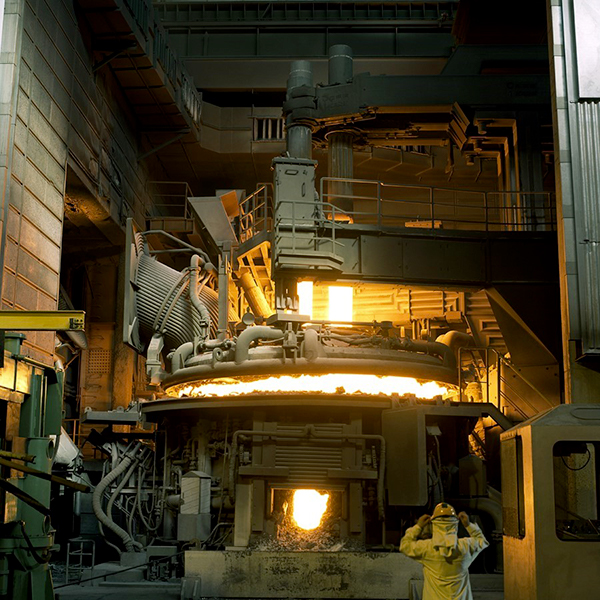
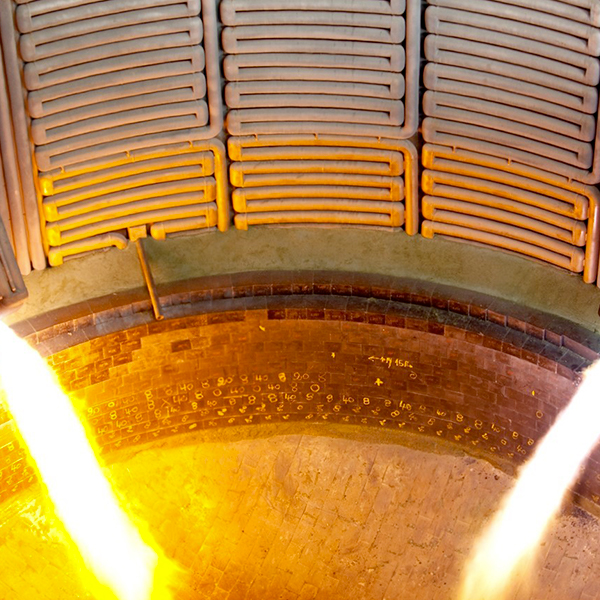
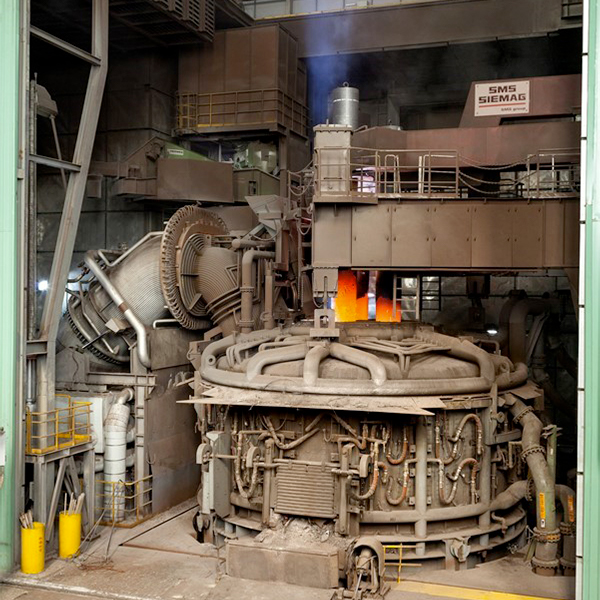
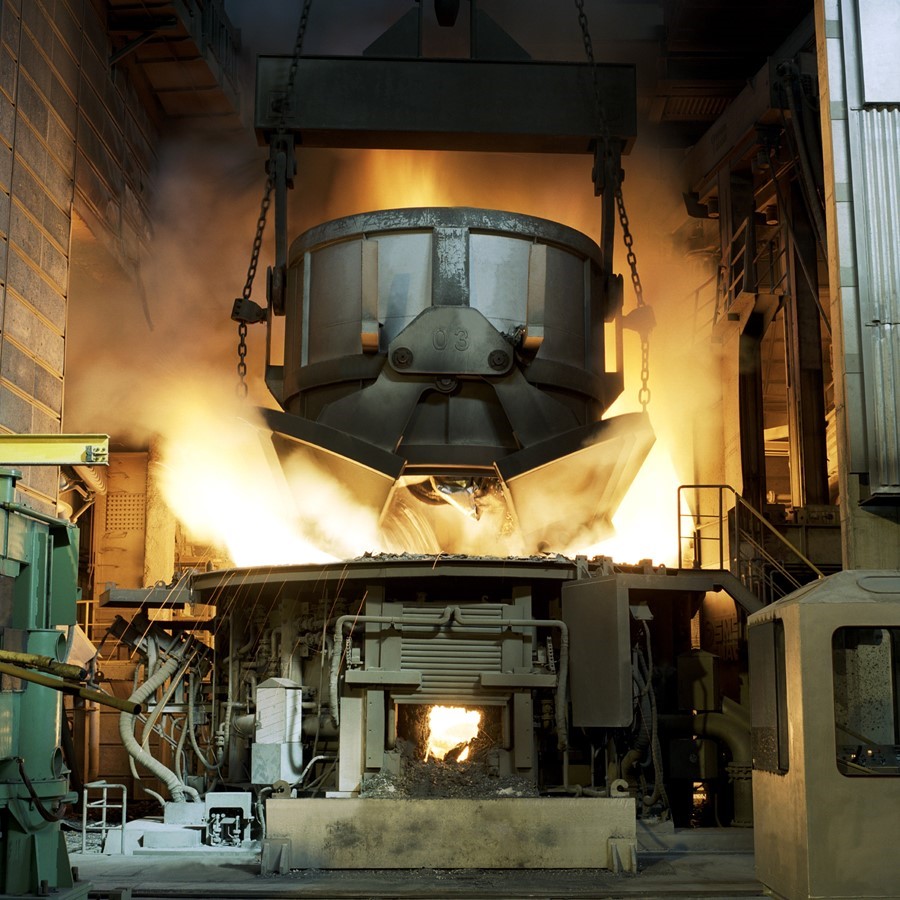
The steel production trough electric arc furnaces (EAF) plays an increasingly important role in modern steelworks concepts. With 81 % in Italy and 61% in Spain, the production of EAF steel is significantly higher than steel production via the blast furnace/basic oxygen furnace route (not considering Member States having exclusively EAF steel production). In the modern EAF, the contribution of the chemical energy for the scrap melting and refining is the range of 25-45% of the total energy required. The Natural Gas (NG) burners provide in the range of 40-80 kWh/t of energy. It means that the production of 100 tons of steel requires the combustion of 370-750 Nm3 of NG with CO2 emission of 0.75-1.5 tons. The substitution of just 10% of NG with hydrogen in the whole steel European production will bring a remarkable reduction of CO2 emission up to 0.1Mtons/year.
In this frame, DevH2forEAF represents a step forward to independence from fossil fuel and bold action to furtherly cut CO2 emissions in steel sectors.
In the 42 months of project duration, the seven partners will face and solve several issues, with the main scope to prove that Hydrogen use in EAF is possible and will be realized. Actions:
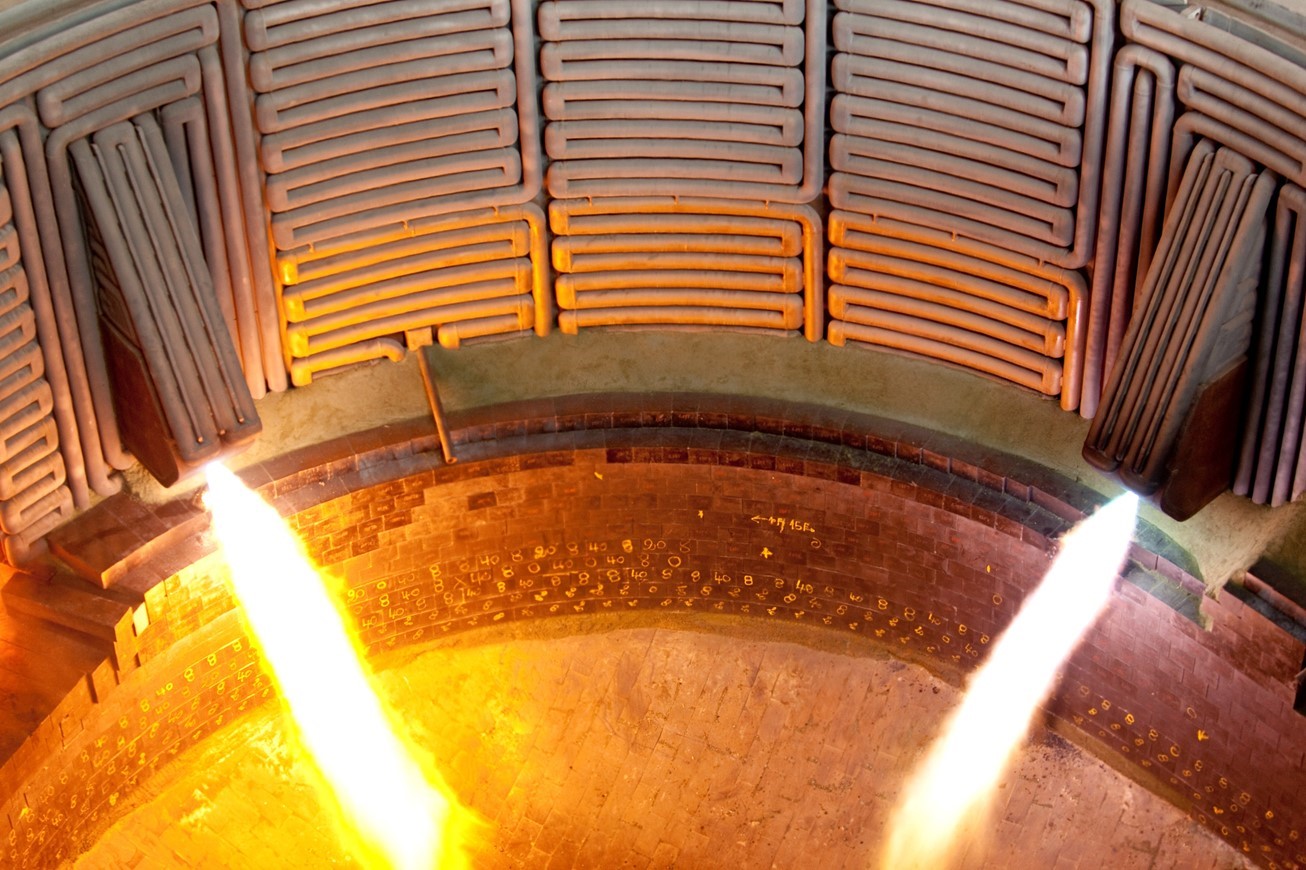
- Design and realization of burners, able to work with NG/H2 mixture, up to 100% hydrogen. The burners will be designed and manufactured to work in severe environment, thus ensuring mechanical and thermal resistance in respect of EAF operative conditions
- Tracking the performance of hydrogen burner in replacement of methane or other carbonaceous fuels through combustion trials in pilot combustion chamber (before industrial installation)
- Investigation of H2 injection on steel quality (pick-up of H2)
- Risk analysis for the definition of the correct actions and countermeasures when hydrogen is used in EAF process: safety issues related to storage, transport and injection must be identified and risks minimized.
- Analysis the performance of hydrogen burner in replacement of NG through experimental trials at two industrial sites (CELSA – Spain and FERRIERE NORD – Italy)
- Analysis of the impacts on environment and safety H2 utilization, enriched by LCA analysis. Detailed economic calculations
The activities are organized in 9 Work Packages, according to the traditional scheme of RFCS funded projects:
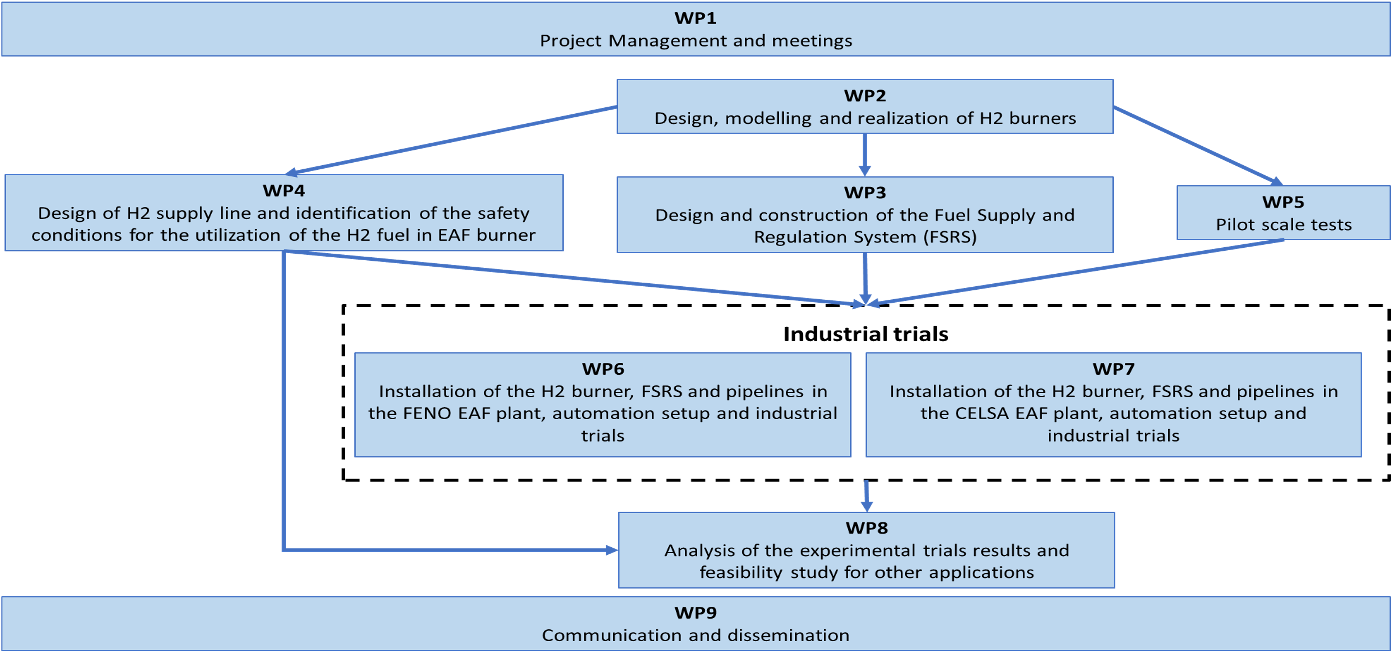
Partners TASKS:
- RINA-CSM is coordinator of the project. Besides management activities and organization of dissemination actions it focuses directly on three areas: combustion chamber tests, experimental campaign and following data analysis. It deals with feasibility study on possible use of hydrogen produced in situ and with predictability analysis of massive use of hydrogen in EAF.
- SMS activaties are related to the design, manufacturing and optimization of burner prototypes and full-scale. It assists CELSA and FENO for the installation of burner on EAF plants. SMS will support experimental campaigns and promote actions to optimize the functionality of EAF burner.
- Nippon Gases tasks concern on the design of hydrogen pipeline, H2 storage tank and as well as safety prescription for burner installation on the industrial sites. Nippon Gases acts also as leader for the risk analysis, producing a management risk plan.
- RWTH-IOB is in charge to investigate the influence of hydrogen combustion system on steel chemistry and EAF operation. Development of thermodynamic and kinetic models and testing with in an EAF pilot plant are its main activities. Finally, it deals with LCA analysis.
- CELSA and FENO are addressed of operative actions, taking care of the installation of the various equipment inside their own plant and handling the experimental campaign. They provide technical information necessary to perform the various design studies.
- BELTRAME has not operative role, but together with RINA-CSM, provides a systemic study for the implementation of the proposed technology in its own plant, considering a relevant use of hydrogen in EAF








